Click HERE To Buy Proscalpin Online ↓
 Safe Use of Proscalpin: Dosage, Side Effects, Precautions
Safe Use of Proscalpin: Dosage, Side Effects, Precautions
Understanding Proscalpin: What It Is and Does
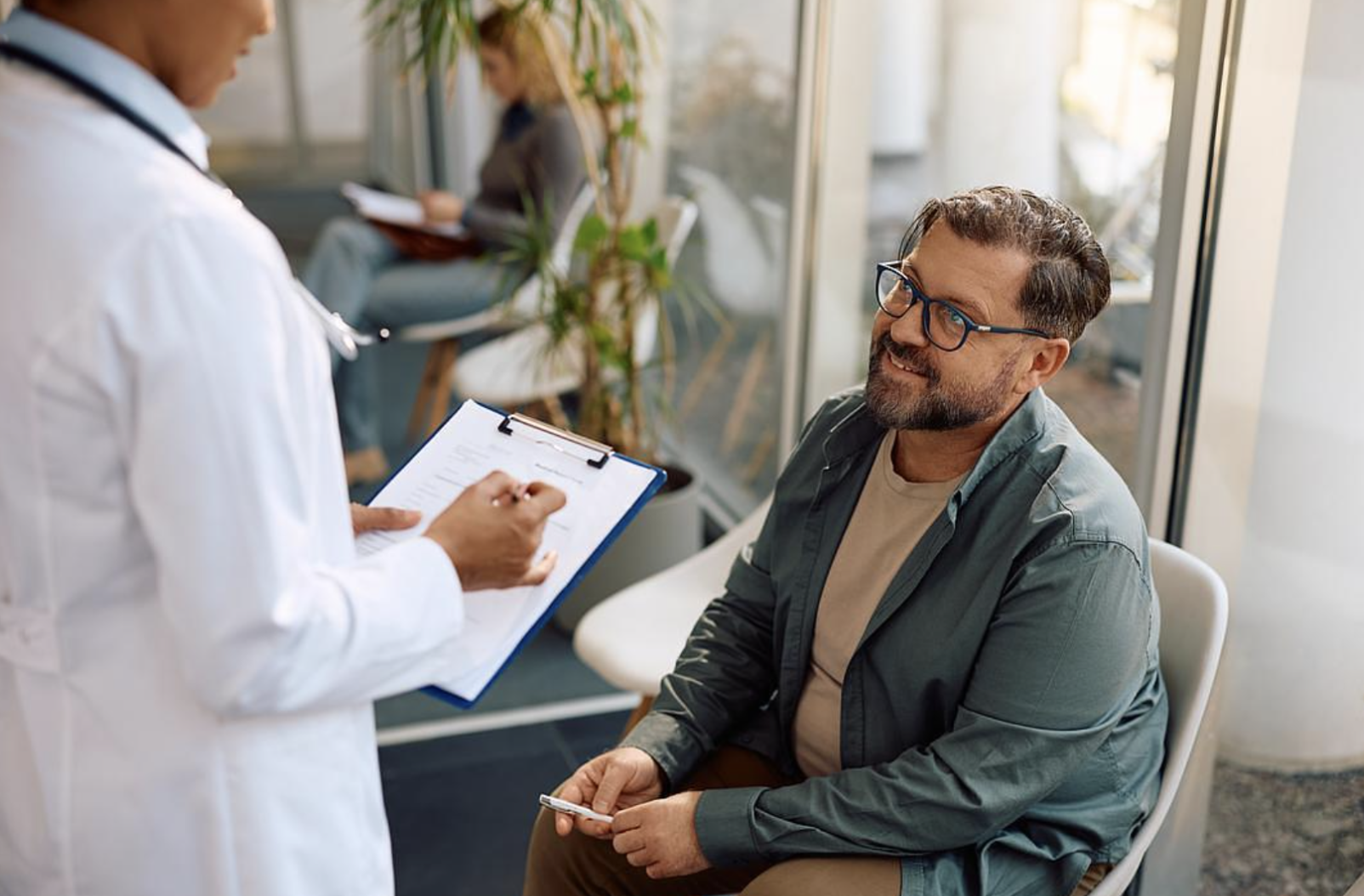
A familiar face at the clinic, Proscalpin is a targeted therapy designed to ease symptoms and modify disease progression in select conditions. Patients often notice improvement within weeks, while clinicians monitor response and adjust plans. The mechanism blends receptor modulation with anti-inflammatory effects to address root causes.
Dosage varies by indication, weight, and comorbidities; prescribers tailor regimens to balance benefit and risk. Common routes are oral and transdermal, with steady dosing recommended to maintain therapeutic levels. Regular blood tests and symptom diaries help track efficacy and detect early adverse reactions.
Discuss risks and benefits, seeking medical advice for personalized guidance.
| Feature | Typical effect |
|---|---|
| Onset | Weeks to months |
| Monitoring | Blood tests, symptom diary |
| Goal | Symptom control and disease modification |
| Side effects | Nausea, headache, dizziness (usually mild) |
| Consult if | Severe reaction, breathing difficulty, swelling |
| Follow-up | Every 1-3 months, then as advised initially |
Recommended Dosage Guidelines: Finding Your Safe Range

When starting proscalpin, imagine tuning an instrument: small adjustments make the melody safe. Physicians usually begin with the lowest effective dose, observing response over days or weeks, then increase cautiously. Never exceed prescribed amounts, and communicate symptoms promptly to your clinician.
For adults, single doses and daily totals vary by condition; follow labeling and doctor instructions closely. Pediatric and elderly dosing often requires reduction and careful monitoring. Use precise measuring devices for liquid forms and avoid splitting extended-release tablets. Maintain a medication diary to track timing and any side effects.
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as remembered unless the next dose is near; do not double up. Discuss renal, hepatic, or cardiovascular history before treatment. Inform your provider about supplements and other prescriptions to prevent interactions. Regular follow-up ensures the chosen regimen remains safe and effective.
Recognizing Side Effects: Mild to Serious Symptoms
A patient remembers the first evening after starting proscalpin: mild nausea and tiredness set in, painting a quiet warning. That early discomfort may be transient or signal sensitivity.
Common effects include headache, dizziness, upset stomach and transient rash; these often resolve within days. If persistent or worsening, contact your provider immediately.
Watch for worsening signs — breathing difficulty, swelling, high fever, severe abdominal pain or fainting — which require immediate care.
Keep a symptom diary, share changes with your clinician promptly, and stop proscalpin if alarming reactions occur; timely action prevents complications.
When to Seek Help: Red Flags and Emergencies

A sudden high fever, severe chest pain, or difficulty breathing after taking proscalpin should be treated as urgent; go to the ER.
Rapid swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, hives, fainting, or unconsciousness may signal anaphylaxis — call emergency services.
Persistent vomiting, uncontrolled bleeding, sudden weakness or numbness on one side, and severe abdominal pain also demand urgent evaluation; bring medication labels and a list of conditions.
If you are unsure, contact poison control or your healthcare provider without delay; timely response often prevents complications and guides correct therapy.
Interaction Risks: Medications, Foods, and Health Conditions
A patient once asked why a single pill could feel different depending on dinner or a cold. The answer lies not in mystery but in chemistry: proscalpin’s effects can be amplified or blunted by other drugs that share metabolic pathways. Understanding which agents compete or potentiate its action prevents surprises.
Some medicines—particularly strong inhibitors or inducers of liver enzymes—change blood levels dramatically, while common foods like grapefruit or alcohol can do the same. Chronic conditions such as liver or kidney disease and heart disorders alter risk thresholds; dosage that was safe before may become risky after new diagnoses.
Before starting or combining therapies, review prescriptions, over-the-counter products, herbal supplements and diet with your clinician. Carry an updated medication list and ask about monitoring plans. Small adjustments or spacing doses can markedly improve safety and preserve proscalpin’s intended benefit and longevity.
| Category | Example |
|---|---|
| Drug | Strong CYP inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) |
| Food | Grapefruit, alcohol |
| Condition | Liver or kidney impairment |
Smart Precautions: Safe Storage, Monitoring, and Follow-up
Treat the medication like a small mission: store it in a cool, dry place away from sunlight and humidity, out of reach of children and pets. Keep it in its original, labeled container to preserve expiration dates and dosing instructions. Avoid bathroom cabinets and freezers unless directed, since temperature extremes can reduce potency and alter formulation.
Monitor response closely: keep a simple log of doses, effects, and any new symptoms, and bring this record to follow-up appointments. Report persistent side effects or changes in mood, sleep, or appetite. Ask your clinician about necessary lab checks or interactions to watch for, and schedule follow-up within the recommended timeframe to reassess safety and effectiveness and adjust dosage. PubMed search: Proscalpin DailyMed search: Proscalpin



